Generative BI and Custom GenAI: The Next Era of Enterprise Data Analytics
Date Published

Generative BI and Custom GenAI: The Next Era of Enterprise Data Analytics
The enterprise analytics landscape is undergoing its most significant transformation in decades. While traditional Business Intelligence tools have served organizations well, they've always suffered from a critical limitation: the need for technical expertise. Today, Generative Business Intelligence (Gen BI) powered by custom GenAI is demolishing this barrier, enabling anyone in your organization to extract insights through simple conversations with data.
But here's what most discussions about Generative BI miss: the difference between generic, off-the-shelf solutions and truly custom GenAI implementations tailored to your proprietary data. This distinction isn't just technical—it's the difference between surface-level analytics and strategic competitive advantage.
Introduction: What is Generative Business Intelligence (Gen BI)?
Generative BI is the application of large language models (LLMs) and other generative AI technologies to automate the process of data analysis, visualization, report creation, and insight generation using natural language inputs.
Unlike traditional BI tools that require users to understand SQL, navigate complex dashboards, or master proprietary query languages, Generative BI allows business users to simply ask questions in plain English—or any natural language. The system interprets the intent, accesses relevant data, performs the necessary analysis, and delivers insights in formats ranging from written summaries to interactive visualizations.
Think of it as having a data analyst available 24/7 who understands your business context, never gets tired, and can process millions of data points in seconds. But the true power emerges when these capabilities are enhanced through custom GenAI—models specifically trained on your organization's unique data, terminology, and business logic.
The Evolution from Traditional to Generative BI
Traditional Business Intelligence emerged in the 1960s and has evolved through several generations—from basic reporting systems to sophisticated self-service analytics platforms. However, even the most advanced traditional BI tools share common limitations:
● Technical barriers: Users need training in specific tools and query languages
● Time-intensive analysis: Building dashboards and reports requires significant manual effort
● Limited flexibility: Pre-built reports can't adapt to unexpected questions
● Insight bottlenecks: Data teams become overwhelmed with ad-hoc requests
Generative BI eliminates these friction points by serving as an intelligent interface between users and data, understanding context, and generating insights on demand.
The Core Architecture: How Generative BI Works Under the Hood
Understanding the technical foundation of Generative BI is essential for making informed implementation decisions. At its core, Gen BI systems combine several advanced technologies:
Large Language Models (LLMs): These neural networks, trained on vast amounts of text data, understand natural language queries and can generate human-like responses. In BI contexts, LLMs translate conversational questions into executable data queries and interpret results into meaningful insights.
Data Connectors: Specialized integrations that allow the Gen BI system to access your data warehouses, cloud storage, operational databases, and SaaS applications. These connectors maintain real-time or near-real-time synchronization with your data sources.
Query Generation Engine: This component translates the LLM's understanding of user intent into actual database queries (SQL, NoSQL, or API calls). It handles the complexity of joining tables, aggregating data, and applying appropriate filters.
Visualization Generator: Rather than just providing text answers, modern Gen BI systems can automatically create charts, graphs, and dashboards that best represent the data being analyzed.
Context Management: The system maintains conversation history and business context, allowing for follow-up questions and iterative analysis without repeating information.
LLMs and Vector Databases in BI Workflows
One of the most critical innovations in custom Generative BI is the integration of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) architectures. Here's how this works:
RAG, or Retrieval-Augmented Generation, uses an organization's proprietary data indexed in a vector database to provide relevant, up-to-date context to the LLM, dramatically improving the accuracy of BI queries.
Instead of relying solely on the LLM's training data (which has a cutoff date and may lack your specific business information), RAG systems first search through your organization's documentation, metadata, and historical queries stored in vector databases. This retrieved context is then provided to the LLM along with the user's question, ensuring responses are grounded in your actual data and business reality.
Vector databases store information as mathematical representations (embeddings) that capture semantic meaning. When a user asks a question, the system finds the most semantically similar information from your data catalog, business glossary, and past analyses—even if the exact words don't match. This semantic search capability is what makes natural language queries so powerful.
The Game Changer: Leveraging Custom GenAI for Proprietary Data
This is where most organizations make a critical strategic error: they assume that general-purpose Generative BI solutions will automatically understand their unique business context, terminology, and data structures. They won't.
Custom GenAI in BI involves fine-tuning or training LLMs on proprietary, domain-specific organizational data to ensure higher accuracy, improve data security, and reduce the risk of hallucinations inherent in general-purpose models.
Consider a pharmaceutical company using the term "pipeline" to refer to drug development stages, while a manufacturing firm uses the same term for production throughput, and an oil and gas company means literal pipelines. A generic Gen BI tool might confuse these contexts, leading to incorrect analyses. A custom GenAI model trained on your specific terminology eliminates this ambiguity.
Fine-Tuning LLMs for Domain-Specific BI (The Customization Layer)
Fine-tuning is the process of taking a pre-trained foundation model and continuing its training on your organization's specific data, including:
Business Terminology and Definitions: Every industry and organization has specialized language. Fine-tuning teaches the model your precise definitions, whether it's understanding that "ARR" means Annual Recurring Revenue in your SaaS company or refers to Absolute Risk Reduction in your healthcare organization.
Historical Query Patterns: By training on past successful queries and analyses, the model learns what types of questions your organization typically asks and what constitutes a "good" answer in your context. This dramatically improves response relevance and reduces the need for query refinement.
Business Logic and Calculations: Organizations have unique ways of calculating key metrics. A custom model can learn that your "Customer Lifetime Value" formula differs from the industry standard, or that your fiscal year starts in July rather than January.
Organizational Structure and Hierarchies: Understanding how your company is organized—divisions, product lines, geographic regions, reporting relationships—allows the Gen BI system to automatically apply appropriate filters and aggregations.
The fine-tuning process typically involves:
- Data Collection: Gathering representative samples of your business documents, data dictionaries, successful past analyses, and expert-annotated examples
- Preprocessing: Cleaning and formatting this data to optimize learning
- Training: Running the fine-tuning process, which adjusts the model's parameters to better predict and generate content in your specific domain
- Validation: Testing the fine-tuned model against held-out examples to ensure it generalizes well
- Iteration: Continuously improving the model as new patterns and terminology emerge
Data Privacy and Security in Private GenAI Deployment
For many enterprises, especially those in regulated industries like healthcare, finance, or government, data security isn't just important—it's mandatory. This is where custom GenAI deployment provides critical advantages over cloud-based, multi-tenant solutions.
Private Deployment Options: Custom GenAI solutions can be deployed entirely within your infrastructure—whether on-premises, in your private cloud, or in a virtual private cloud (VPC) with strict network isolation. Your data never leaves your security perimeter.
Data Minimization: Unlike generic solutions that may need to send entire datasets to external APIs for processing, custom models can be optimized to work with data summaries, aggregations, or synthetic data that preserves statistical properties while protecting sensitive details.
Access Control Integration: Custom deployments integrate seamlessly with your existing identity and access management systems, ensuring that the Gen BI system respects row-level security, column-level permissions, and role-based access controls that you've already established.
Audit Trails and Compliance: Private deployments allow you to maintain complete logs of all queries, data accessed, and insights generated—essential for regulatory compliance in industries like healthcare (HIPAA), finance (SOX, GDPR), and government (FedRAMP).
Encryption and Key Management: You maintain control over encryption keys and can implement end-to-end encryption that ensures data remains protected at rest, in transit, and even during processing.
The security advantage of custom GenAI isn't just about preventing data breaches—it's about maintaining competitive advantage. Your proprietary data, insights, and analytical patterns remain yours alone, rather than potentially contributing to the training data of shared models that competitors might also access.
Generative BI vs. Traditional BI: A Direct Comparison
Understanding the fundamental differences between these approaches helps clarify why organizations are making the shift:
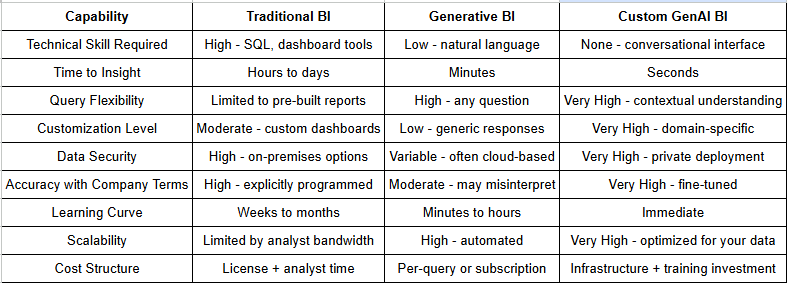
The progression from Traditional to Generative to Custom GenAI BI represents increasing levels of democratization, speed, and contextual intelligence—but also increasing implementation complexity. The key is matching the solution to your organization's specific needs and capabilities.
Key Benefits of a Custom Generative BI Implementation
While generic Generative BI tools offer clear advantages over traditional systems, custom implementations unlock transformational benefits that justify the additional investment:
Enabling True Self-Service Analytics for Non-Technical Users
The promise of "self-service BI" has existed for years, but traditional tools still required significant training and technical aptitude. Custom Generative BI delivers on this promise by:
Eliminating the Query Language Barrier: Marketing managers can ask "Which campaigns drove the highest customer lifetime value last quarter?" without understanding JOIN operations or aggregate functions. The system translates their intent into proper queries automatically.
Understanding Organizational Context: A custom model knows that when someone in Sales asks about "pipeline," they mean sales opportunities, while someone in Manufacturing means production flow. Generic tools would require clarification; custom models understand implicitly.
Reducing Data Team Bottlenecks: According to industry research, data analysts spend 60-80% of their time answering repetitive ad-hoc questions from business users. Custom Gen BI automates these routine inquiries, allowing data teams to focus on complex strategic analyses.
Providing Guided Discovery: Custom models can proactively suggest relevant follow-up questions based on your organization's analytical patterns, helping users discover insights they didn't know to ask about.
Accelerating Time-to-Insight (From Days to Seconds)
Speed isn't just about convenience—it's about competitive advantage:
Real-Time Decision Making: When a customer success manager notices unusual churn patterns during a client call, they can immediately query the Gen BI system to understand contributing factors and propose solutions—all within the same conversation.
Iterative Analysis: Traditional BI requires submitting a query, waiting for results, then formulating the next question. Custom Gen BI maintains conversational context, allowing rapid iteration: "Now break that down by region" → "Show me the same analysis for last year" → "Which products contributed most to the difference?"
Automated Insight Generation: Rather than waiting for scheduled reports, custom Gen BI systems can proactively monitor your data and alert stakeholders when significant patterns emerge, providing immediate context and suggested actions.
Reduced Report Development Time: Creating a comprehensive dashboard in traditional BI tools can take days or weeks. Custom Gen BI can generate equivalent visualizations and insights in minutes based on natural language specifications.
Practical Custom Gen BI Use Cases Across the Enterprise
The versatility of custom Generative BI means value creation across every business function:
Finance and Accounting
Budget Variance Analysis: CFOs can ask "Explain why our operational expenses in EMEA exceeded budget by 15% in Q3" and receive a detailed breakdown showing that increased cloud infrastructure costs and unexpected currency fluctuations were primary drivers, with suggestions for mitigation.
Financial Forecasting: Custom models trained on historical financial data can generate scenario-based forecasts: "Project our cash position for the next six quarters assuming 10% revenue growth and current burn rate." The system understands your specific chart of accounts and accounting policies.
Audit and Compliance: "Identify all transactions over $50,000 that didn't follow standard approval workflows" becomes a simple query rather than a complex SQL investigation, with results properly contextualized using your organization's approval hierarchies.
Marketing and Customer Analytics
Campaign Performance Analysis: Marketing directors can query "Compare ROI across all channels for our product launch campaign, and recommend budget allocation for next quarter based on customer acquisition cost and lifetime value." The system understands your specific attribution model and customer value calculations.
Customer Segmentation: "Show me characteristics of customers who churned within 90 days versus those who remained for over two years" generates insights using your organization's specific customer data fields and business definitions of churn.
Content Performance: "Which blog topics drive the highest quality leads for our enterprise segment?" The Gen BI system understands your lead scoring model and can trace content engagement through your entire funnel.
Sales and Revenue Operations
Pipeline Health Assessment: Sales VPs can ask "Are we on track to hit our quarterly target?" and receive not just a yes/no answer, but detailed analysis of pipeline velocity, conversion rates by stage, and specific at-risk opportunities requiring attention.
Territory Optimization: "Which territories are underperforming relative to market potential, and what factors contribute to the gap?" The custom model understands your territory definitions, market sizing methodology, and relevant performance metrics.
Win/Loss Analysis: "What patterns distinguish deals we won versus those we lost to competitors in the healthcare vertical?" Custom Gen BI can analyze CRM data, call transcripts, and proposal information using your specific competitive framework.
Operations and Supply Chain
Inventory Optimization: Operations managers can query "Predict stockout risk for high-velocity products over the next 30 days given current lead times and demand trends." Custom models understand your specific SKU structures, supplier relationships, and seasonal patterns.
Quality Analysis: "Identify common factors in products with defect rates above 2% across all manufacturing lines." The system knows your specific quality metrics, production processes, and acceptable thresholds.
Capacity Planning: "At what point will our fulfillment capacity become constrained given projected order growth?" Custom Gen BI can factor in your specific operational constraints, staffing models, and throughput rates.
Human Resources and Talent Analytics
Retention Analysis: HR leaders can ask "Which departments have the highest flight risk, and what are the common factors among employees likely to leave?" The system respects privacy while identifying actionable patterns in tenure, compensation, engagement scores, and career progression.
Compensation Benchmarking: "Are our senior engineer salaries competitive with market rates in our key hiring locations?" Custom models understand your specific job levels, geographic markets, and compensation philosophy.
Skills Gap Analysis: "What skills gaps will we face if we pursue our expansion into the Asia-Pacific region, and how can we address them?" The Gen BI system analyzes your current workforce capabilities against strategic requirements.
Addressing the Risks: Hallucinations, Bias, and Governance
No discussion of Generative BI would be complete without addressing its limitations and risks. Organizations must implement proper safeguards to ensure reliability:
The Hallucination Problem
The primary risk is data hallucinations—where the AI provides incorrect or misleading insights based on faulty logic or inaccurate data interpretation—which is exacerbated by poor data governance or lack of context.
LLMs are trained to generate plausible-sounding text, not necessarily accurate information. In BI contexts, this can manifest as:
● Fabricated Data Points: The model might report specific numbers that seem reasonable but don't exist in your data
● Misinterpreted Relationships: Confusing correlation with causation or suggesting relationships between unrelated metrics
● Outdated Information: Providing insights based on the model's training data rather than current data
● Confident Errors: Presenting incorrect analysis with high confidence, making it difficult for users to recognize problems
Mitigation Strategies for Custom GenAI:
- Grounding in Actual Data: RAG architectures ensure responses are based on retrieved facts rather than generated speculation
- Confidence Scoring: Custom models can be trained to provide uncertainty indicators: "Based on limited historical data, predicted revenue could range from X to Y with moderate confidence"
- Citation Requirements: Configure the system to always cite specific data sources and timestamps for factual claims
- Human-in-the-Loop Validation: For high-stakes decisions, implement approval workflows that require expert review before action
- Adversarial Testing: Regularly test the system with questions designed to expose hallucinations, using these findings to improve the model
Bias and Fairness Concerns
AI systems can perpetuate or amplify biases present in training data:
Historical Bias: If past hiring data shows preferences for certain demographics, an untrained Gen BI system might identify these patterns as "success factors" rather than historical discrimination
Representation Bias: Underrepresented groups in training data may receive less accurate analysis
Measurement Bias: Differences in how data is collected across groups can lead to misleading conclusions
Custom GenAI Mitigation:
● Bias Audits: Regularly analyze model outputs across protected categories to identify disparate impact
● Fairness Constraints: Implement technical constraints ensuring certain protected attributes don't inappropriately influence recommendations
● Diverse Training Data: Ensure fine-tuning datasets include representative samples across all relevant dimensions
● Explainability: Custom models can be designed to explain their reasoning, making bias identification easier
Data Governance and Responsible AI Frameworks
Successful custom Gen BI implementations require robust governance:
Access Control Policies: Define who can query what data, ensuring the Gen BI system respects existing row-level and column-level security
Query Auditing: Maintain comprehensive logs of all questions asked, data accessed, and insights generated for compliance and security monitoring
Data Quality Requirements: Establish minimum standards for data completeness, accuracy, and freshness before making sources available to Gen BI
Model Monitoring: Continuously track model performance metrics including accuracy, response time, hallucination rate, and user satisfaction
Ethical Guidelines: Document acceptable use cases and prohibited applications, ensuring the technology aligns with organizational values
Version Control: Maintain clear versioning of models, training data, and configurations to enable rollback if issues emerge
Incident Response: Establish clear protocols for addressing hallucinations, security concerns, or ethical violations when they occur
Making the Decision: Build Your Own vs. Buy a Platform
This is perhaps the most critical strategic decision organizations face when implementing Generative BI:
When to Buy an Existing Platform
Commercial Gen BI platforms (like those from IBM, Domo, Pyramid Analytics, or emerging startups) make sense when:
Speed to Value is Critical: You need Gen BI capabilities operational within weeks rather than months Limited Internal AI Expertise: Your organization lacks deep learning engineers and LLM specialists Standard Use Cases: Your needs align well with industry-standard business intelligence patterns Smaller Data Volumes: Your data infrastructure is relatively straightforward and well-structured Limited Customization Needs: Industry-standard terminology and business logic work for your context Budget Constraints: Your organization can't justify the significant investment in custom development
Advantages: Fast implementation, proven technology, ongoing vendor support, regular feature updates Disadvantages: Less customization, potential security concerns, recurring licensing costs, dependency on vendor roadmap
When to Build Custom GenAI Solutions
Custom development makes sense when:
Highly Specialized Domain: Your industry or organization uses terminology and logic that differs significantly from standards (pharmaceutical R&D, defense contracting, proprietary trading strategies) Strict Security Requirements: Regulatory or competitive concerns mandate private deployment with complete data control Unique Competitive Advantage: Your analytical capabilities are a core differentiator, and exposing query patterns to external vendors creates risk Complex Data Environments: Your data architecture is highly customized, making integration with standard platforms difficult Significant Scale: At high query volumes, custom solutions become more cost-effective than per-query commercial pricing Long-Term Strategic Investment: You view AI capabilities as foundational to your business and want to build institutional knowledge
Advantages: Perfect alignment with business needs, maximum security, no vendor lock-in, potential competitive differentiation Disadvantages: Higher upfront investment, longer implementation timeline, ongoing maintenance responsibility, requires specialized talent
The Hybrid Approach
Many organizations find success with a hybrid strategy:
- Start with Commercial Platform: Deploy a commercial Gen BI solution for standard use cases to demonstrate value quickly
- Identify Customization Needs: As usage scales, identify specific areas where customization would deliver significant additional value
- Selective Custom Development: Build custom models for high-value, differentiated use cases while maintaining the commercial platform for routine analytics
- API Integration: Use the commercial platform's infrastructure while enhancing it with custom models for domain-specific understanding
This approach balances speed, risk, and customization while building internal capabilities over time.
Implementing Custom Generative BI: A 5-Step Workflow
For organizations choosing custom development, here's the proven implementation path:
Step 1: Data Integration and Preparation
Objective: Establish comprehensive, high-quality data access for the Gen BI system
Key Activities:
● Source Identification: Catalog all relevant data sources including data warehouses, operational databases, cloud storage, SaaS applications, and unstructured documents
● Connection Architecture: Implement secure connectors with appropriate authentication, encryption, and network isolation
● Data Quality Assessment: Evaluate completeness, accuracy, consistency, and freshness of each source
● Metadata Documentation: Create comprehensive data dictionaries explaining each field's meaning, valid values, and business context
● Governance Framework: Establish policies for data access, retention, privacy, and quality standards
Success Metrics: All critical data sources connected, data quality issues documented with remediation plans, comprehensive metadata catalog
Step 2: LLM Selection and Architecture Design
Objective: Choose the optimal model foundation and design the technical architecture
Key Decisions:
● Foundation Model Selection: Evaluate options like GPT-4, Claude, LLaMA, or domain-specific alternatives based on performance, cost, and licensing
● Deployment Model: Decide between API-based access, private cloud deployment, or on-premises hosting
● RAG Architecture: Design vector database architecture for efficient semantic search across your data catalog and documentation
● Integration Approach: Determine how Gen BI will integrate with existing BI tools, data visualization platforms, and business applications
Technical Components:
● Vector database (Pinecone, Weaviate, or self-hosted alternatives)
● Query generation layer
● Response formatting and visualization engine
● Conversation management system
● Security and access control layer
Success Metrics: Architecture documentation complete, proof-of-concept demonstrating end-to-end workflow, performance benchmarks established
Step 3: Model Fine-Tuning and Customization
Objective: Adapt the chosen foundation model to your organization's specific context
Training Data Collection:
● Business glossaries and terminology documents
● Historical successful queries and their results
● Domain-specific documentation and knowledge bases
● Expert-annotated example conversations
● Business logic and calculation definitions
Fine-Tuning Process:
● Preprocess training data into optimal format
● Configure fine-tuning parameters (learning rate, epochs, batch size)
● Execute training runs with validation monitoring
● Evaluate results against held-out test sets
● Iterate based on performance metrics
Customization Layers:
● Domain-specific terminology understanding
● Business logic and calculation rules
● Organizational structure and hierarchies
● Industry-specific compliance requirements
● User role and permission awareness
Success Metrics: Model accuracy on domain-specific queries exceeds 90%, hallucination rate below acceptable threshold, response time meets SLA targets
Step 4: Secure Deployment and Integration
Objective: Make the custom Gen BI solution available to users while maintaining security
Deployment Activities:
● Infrastructure Setup: Provision computing resources (GPUs for model serving, vector database hosting, application servers)
● Security Implementation: Configure encryption, access controls, network isolation, and audit logging
● Integration Development: Connect Gen BI to existing tools (BI platforms, collaboration apps, workflow systems)
● User Interface Creation: Develop chat interfaces, Slack/Teams bots, or embedded analytics components
● Testing: Conduct comprehensive security testing, performance testing, and user acceptance testing
Integration Points:
● Business intelligence platforms (Tableau, Power BI)
● Collaboration tools (Slack, Microsoft Teams)
● Workflow automation (Zapier, Make)
● Business applications (CRM, ERP systems)
● Data visualization libraries
Success Metrics: System available to pilot users, security audit passed, performance meets defined SLAs, integration with key tools functional
Step 5: Governance and Continuous Monitoring
Objective: Ensure ongoing reliability, accuracy, and value delivery
Governance Framework:
● Query Monitoring: Track all queries, data accessed, and response quality
● Accuracy Measurement: Randomly sample responses for expert validation
● Hallucination Detection: Implement automated checks for impossible values or contradictory statements
● Bias Monitoring: Regular audits of outcomes across demographic and other sensitive dimensions
● Security Surveillance: Continuous monitoring for unauthorized access attempts or policy violations
Continuous Improvement:
● Collect user feedback on response quality and relevance
● Identify common query patterns for further optimization
● Periodically retrain models on new data and organizational changes
● Update business logic and terminology as the organization evolves
● Expand capabilities based on user needs and new technologies
Success Metrics: User satisfaction above 85%, hallucination rate trending downward, query volume growing month-over-month, demonstrable business impact
Conclusion: The Future is Custom and Conversational
The evolution from traditional Business Intelligence to Generative BI represents more than a technological upgrade—it's a fundamental reimagining of how organizations interact with data. While generic Gen BI tools offer compelling advantages over legacy systems, custom GenAI implementations deliver transformational value for organizations with unique requirements, complex data environments, or strategic advantages tied to analytical capabilities.
The key insights driving successful implementations:
Democratization at Scale: Custom Gen BI finally delivers on the long-promised vision of self-service analytics. By understanding your specific business context, it enables every employee—from entry-level analysts to C-suite executives—to extract insights without technical barriers.
Security Without Compromise: Organizations no longer must choose between AI-powered innovation and data security. Private deployment of custom models ensures your most sensitive data and competitive insights remain under your complete control.
Accuracy Through Specificity: Generic models struggle with domain-specific terminology and business logic. Custom fine-tuning eliminates ambiguity, reducing hallucinations and ensuring insights align with your organizational reality.
Speed as Competitive Advantage: When decision-makers can get answers in seconds rather than days, the entire organization becomes more agile, responsive, and competitive. The compound effect of thousands of accelerated decisions creates measurable business impact.
Taking the First Step
Whether you choose a commercial platform, build a custom solution, or pursue a hybrid approach, the critical factor is starting your Generative BI journey now. Organizations that delay risk falling behind competitors who are already leveraging conversational analytics to make faster, better-informed decisions.
For most enterprises, the optimal path forward involves:
- Pilot with High-Value Use Case: Select a specific department or business function where Gen BI can demonstrate clear ROI quickly
- Build Internal Expertise: Invest in training your data teams on LLM technologies, prompt engineering, and RAG architectures
- Establish Governance Early: Don't wait until you have problems—implement monitoring, auditing, and ethical guidelines from day one
- Plan for Scale: Design your initial implementation with expansion in mind, ensuring architecture can grow across the organization
- Measure and Iterate: Define clear success metrics and continuously refine based on user feedback and performance data
The Strategic Imperative
The question is no longer whether to adopt Generative BI, but how to implement it in a way that maximizes value while managing risk. Custom GenAI represents the most sophisticated approach, offering unparalleled alignment with organizational needs, but requiring significant investment and expertise.
For organizations where data analytics drives competitive advantage, where proprietary terminology and business logic create complexity, or where security requirements mandate private deployment, custom GenAI isn't just an option—it's a strategic necessity.
The enterprises that will dominate the next decade are those that can turn data into insights, and insights into action, faster than their competitors. Custom Generative BI is the enabler of this transformation, making conversational analytics not just possible, but powerful, secure, and precisely aligned with your business reality.
Ready to Build Your Custom GenBI Solution?
The future of enterprise analytics is conversational, intelligent, and custom-tailored to your organization's unique needs. Whether you're just beginning to explore Generative BI or ready to move beyond generic solutions to custom implementation, the journey starts with understanding your specific requirements and building the right foundation.
Key considerations as you move forward:
● Assess your current data infrastructure maturity
● Identify high-impact use cases where custom capabilities deliver differentiated value
● Evaluate your internal AI/ML expertise and gaps
● Define your security and compliance requirements
● Establish clear ROI metrics for measuring success
The convergence of large language models, vector databases, and domain-specific fine-tuning has created an unprecedented opportunity to reimagine how organizations interact with data. Custom Generative BI transforms data from a static resource into an active, conversational partner in decision-making—one that speaks your language, understands your business, and accelerates your competitive advantage.
The question isn't whether AI will transform business intelligence. It's whether your organization will lead that transformation or follow it.